7 Top 3D Printed Prosthetics & Leading Companies

The widespread availability of and increasing performance of 3D printing technologies has led to an explosive development in the prosthetics sector in the last decade. Increasingly customized and patient-unique solutions are being developed by a spectrum of suppliers who all aim for customized and cost-effective solutions that are adjusted to the particular needs of the individual. These businesses fall between truly commercial and charitable. Their services are intended to be highly patient-enabling first, with a common theme being that they exist first to serve and then to profit.
Listed below are some of the top 3D-printed prosthetics and the leading companies of this expertise:
1. 3D Printed Prosthetic Feet
3D-printed prosthetic feet offer patient-customizable and cost-effective solutions for lower limb amputees. The demand in this area is increasing with the incidence of diabetes, which too often results in foot amputations.
Using advanced additive-manufacturing methodologies, these prosthetics can be tailored to individual patient specifications with relatively low effort. 3D printing allows for greater complexity of functional designs and design iterations to be made quickly without excessive complexity/delay in making new parts. These provide comfortable and functional replacements for lost limbs without the cost of traditional methods. They aim to be lightweight and durable and are intended (somewhat) to mimic the natural movement of a foot. This recreates mobility and improves the quality of life for users.
2. 3D Printed Prosthetic Hands
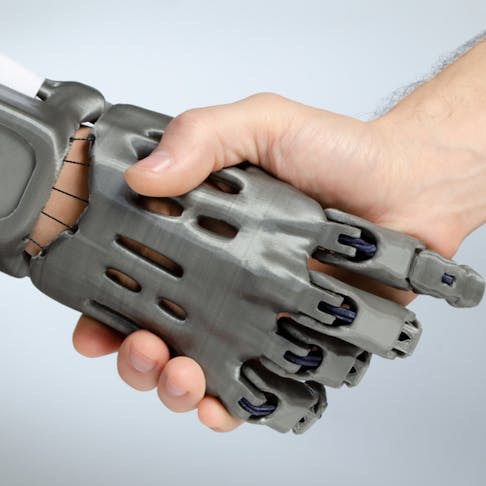
3D-printed prosthetic hands offer customizable and cost-effective solutions for amputees with high functionality and increasingly close-to-real-use scenarios. These prosthetics are typically designed to closely mimic the functionality and appearance of natural hands. The use of skin sensors to allow users to control hand movements is reported as so closely integrated with patient behaviors that phantom pains diminish or disappear, once the user becomes skilled in the device use.
Unlike traditional prosthetics, which are often one-size-fits-all, 3D printing allows for personalized design adjustments to accommodate unique anatomical features and functional requirements. Quick iterations of the design are also made possible by 3D printing. This process also significantly reduces the lead time associated with traditional prosthetic manufacturing methods. Additionally, 3D-printed prosthetic hands are lightweight and durable, making them comfortable to wear for extended periods and suitable for everyday activities. The materials used in 3D printing, such as thermoplastics and laser-sintered metals, offer both strength and flexibility. Figure 1 below shows a 3D-printed prosthetic hand being demonstrated:
3D printed hand.
Image Credit: Shutterstock.com/Reshetnikov_art
3. 3D Printed Prosthetic Arms
3D-printed prosthetic arms provide customizable fitment and functional solutions for individuals with upper limb amputations or differences. Using cutting-edge additive-manufacturing techniques, these prosthetics are tailored to the particular anatomical requisites of the individual who wears them.
They offer lightweight, durable, and comfortable alternatives to prosthetics made by more typical and less flexible methods. These options use polymers, metal-joint parts as required, and carbon-fiber structures. This serves to deliver strength and flexibility, and the digital-manufacturing aspects allow for personalization in design adjustments to be made quickly, ensuring a comfortable fit.
These prosthetic arms enable users to perform an effectively typical range of daily activities, including grasping complex and delicate objects, eating, and even playing musical instruments in some cases, improving the quality of life for amputees worldwide. Figure 2 below shows a woman with a 3D-printed prosthetic arm:
3D printed arm.
Image Credit: Shutterstock.com/shurkin_son
4. 3D Printed Prosthetic - Facial
3D-printed prosthetic facial devices are innovative solutions for individuals with facial disfigurement or abnormality. These are generally produced through 3D printing techniques, allowing for precise customization to reflect the unique contours and features of each patient's normal face. 3D scanning can play a significant part in the personalization process, reproducing and mirroring more-normal facial features without the need for skilled or artistic interpretation.
Made from biocompatible materials like silicone rubber or medical-grade polymers, 3D-printed facial prosthetics offer some degree of normative appearance and comfortable fit. They can restore symmetry, improve facial aesthetics, and most importantly enhance the self-confidence of patients with conditions such as: facial paralysis, congenital defects, or injuries. Figure 3 below shows a 3D-printed human lower jaw:
3D printed lower jaw.
Image Credit: Shutterstock.com/MarinaGrigorivna
5. 3D Printed Prosthetic Knee
3D-printed prosthetic knees are designed to restore mobility and improve the quality of life for individuals with lower-limb amputations. Using additive-manufacturing technology, these prosthetics are customized to fit the unique anatomy and activity level of individual patients.
They are crafted from durable and lightweight materials, such as titanium for joint parts and carbon fiber for structural elements, to provide stability and support while minimizing weight. 3D printing allows for designs that integrate adjustable joint mechanisms and shock-absorbing components, to enhance comfort, functionality, and durability. These prosthetic knees commonly enable users to walk, run, and engage in normal physical activities with confidence and ease, restoring the ability to lead active and fulfilling lives.
6. 3D Printed Prosthetic Legs
Components for 3D-printed prosthetic legs deliver novel approaches to individualization with lower-limb amputees, providing a degree of customization for functional replacements for lost limbs. Such devices must be tailored to the unique anatomy, activity level, and preferences of individual users to be useful to the wearer.
Prosthetic legs typically consist of the socket components, pylon, and foot, any of which can be individually customized using 3D printing technology. Additive manufacturing allows for the possible incorporation of complex geometries and lightweight materials, such as carbon fiber or titanium, to optimize the strength-to-weight ratio and overall performance. The more traditional one-type-for-all approach inevitably limits function and aesthetics. Various design aspects, including energy-storing prosthetic feet for a rebound in the stride or multi-axial dynamic response aspects, can be tailored to accommodate the activity levels and gait patterns of individuals. In particular, the customization aspects, when delivered by more traditional hand-crafted methods are extremely slow and reliant on a few skilled technicians, whereas 3D-printed customization can be delivered very fast.
7. Other 3D-Printed Prosthetics
3D-printed prosthetic hips are designed to replace or augment the function of the hip joint in individuals with hip dislocations, degenerative joint disease, or traumatic injuries. These prosthetics offer improved mobility and stability while reducing pain and discomfort. 3D-printed spinal braces or orthoses serve to support and stabilize the spine in individuals with scoliosis, spinal and spinal-cord injuries, or other diseases or congenital spinal conditions. These devices are necessarily customized to the patient's spinal-curvature profile and are worn to improve posture and mobility.
3D-printed cranial prosthetics assist in reconstructing or replacing parts of the skull in individuals with craniofacial defects, traumatic injuries, or surgical resections. 3D-printed prosthetics for the torso, such as chest wall or abdominal supports, are some other examples. They are used to provide temporary or permanent support and protection for individuals with thoracic or abdominal injuries, deformities, or surgical interventions. 3D-printed dental prosthetics such as: crowns, bridges, dentures, and orthodontic devices are used to restore, realign, or replace missing teeth and improve oral function and aesthetics. Figure 4 below shows the 3D-printed dental prosthetics concept:
3D printed dental prosthetics.
Image Credit: Shutterstock.com/INTHEBLVCK
What Are 3D Printed Prosthetics?
3D-printed prosthetics are wearable body parts that provide those with physiological divergences, disease-based disabilities, or amputations with a degree of comfort and normality. These customized prosthetics are a perfect case for the more-robust 3D printing technologies. They widely employ one-off designs that are custom fitments to patients while using mass-produced and lower-cost components such as: joint parts, simple “bone” substitutes, and electronics, whenever possible.
To learn more, see our full guide on 3D Printing in Prosthetics.
What Are Common 3D-Printed Prosthetic Materials?
Common materials used in 3D-printed prosthetics include:
- Polylactic acid (PLA)
- Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)
- Polyamide (PA) or Nylon 12
- Photopolymer resins
- Carbon fiber-reinforced composites
- Medical-grade silicone rubber
To learn more, see our full guide on 3D Printing Materials.
What Type of 3D Printing Is Commonly Used in 3D Printed Prosthetics?
The types of 3D printing commonly used in 3D-printed prosthetics are powder bed fusion (PBF) and fused deposition modeling (FDM®). FDM® and fused filament fabrication (FFF) are used for producing plastic prosthetic components such as joint sockets or cosmetic covers. SLA and SLS are also used for printing plastic prosthetic components.
The options for appropriate techniques depend on: the desired material properties for the functional need, part complexity, resolution requirements, availability of services, and production volume. Metal additive manufacturing methods like DMLS and SLM are applicable for their high strength and precision, while plastic printing methods like: FDM®, SLA, and SLS offer greater cost-effectiveness at the expense of strength and durability.
What Are the Pros and Cons of 3D Printing Prosthetics?
3D printing is widely reported in the media as mass production on the desktop. While these rapidly developing technologies provide radical solutions to the rapid making of components, they often need to catch up to expectations. Great care is required in the selection of procedures, materials, and design adaptations to suit the process and the relative cost implications.
As a rule, 3D-printed prosthetic parts, relative to traditional manufacturing processes, are:
- Weaker
- Less durable
- Of poorer surface finish
- Much faster and lower cost to customize
- Available on short lead times
- Often lower acquisition cost, though this may be less significant when a total cost of ownership is considered.
Do 3D-Printed Prosthetics Use Additive Manufacturing?
3D printing and additive manufacturing are essentially the same thing. However, from some viewpoints, 3D printing refers narrowly to FDM® and FFF, so care should be taken in general understanding of terminology. It is increasingly common for prosthetics manufacturers to apply 3D printing prosthetic components to the creation of patient-specific and custom parts for prosthetics while looking to larger volume, lower cost, and more-robust manufacturing processes for the less-customized components. This mix of technologies delivers a better wearer/user experience and a longer-lasting product on a lower budget.
How To Choose the Best 3D Printing Prosthetics
Selecting the optimal material/process for 3D printing components for prosthetics involves prioritizing a variety of factors such as:
- Select materials that meet the prioritized properties: strength, flexibility, biocompatibility, cost, cosmetics, durability, and weight. For example, for structural components, titanium, aluminum/magnesium, or stainless steel offer high performance and durability with options as to weight and cost. Thermoplastics like nylon or PLA are commonly discussed for sockets and cosmetic covers due to their light weight and flexibility.
- Select the optimal 3D printing technology derived from the material requirements, part complexity, process availability, and resolution demanded. For metal components, DMLS, PBF, or SLM are preferred, while FDM®, SLA, or SLS are preferred options for plastic components.
- Determine the levels of customization needed for the prosthetic devices and particular components. Ensure that the chosen printing method can accommodate the required level of customization.
- Evaluate the durability and functional capability of the printed components, particularly for load-bearing, sliding/moving, or abrasion-vulnerable parts.
- Consider the cost and lead-time implications of the opted-for manufacturing methods and materials.
Where To Buy the Best 3D Printing Prosthetics
Identifying high-capability/quality suppliers of 3D printing prosthetics involves researching reputable manufacturers, distributors, and specialist providers. A brief guide is discussed below:
- Look for prosthetic clinics with expertise in 3D printing technology and a track record of delivering customized prosthetic solutions.
- Perform research into well-known manufacturers that offer a range of 3D-printed prosthetic options and have a reputation for quality and innovation.
- Explore online marketplaces specializing in medical devices and prosthetics, on which you can find a variety of 3D-printed prosthetic products from different vendors. Look for happy-client references and make sure you can try before you buy.
- Consider purchasing directly from prosthetic designers and engineers who offer customized 3D-printed prosthetics tailored to individual needs and preferences.
What Are the Best 3D Printing Prosthetics Companies?
Some of the best 3D printing prosthetics companies and products are:
1. Halo
Halo 3D Printed Prosthetics is a product from Limbitless Solutions, a well-reported company with a profile that emphasizes the design and manufacturing of custom 3D-printed prosthetics derived from video game forms. They exploit leading-edge additive manufacturing technology to execute highly personalized prosthetics.
Halo's market-presented solutions are highly appreciated for their innovative approach, exceptional quality, and commitment to improving the lived experiences of amputees and the differently-limbed worldwide. Halo’s focus on innovation and excellence has earned them a reputation as a trusted leader in 3D-printed prosthetics.
2. Kinetic
Kinetic 3D Printed Prosthetics is a pioneering product from the charity Free 3D Hands, a team dedicated to progressing prosthetic technologies through the application of additive manufacturing. Kinetic exploits the more advanced capabilities of 3D printing to build highly customized solutions for individual clients with limb differences.
Their prosthetics are widely appreciated for their precision, durability, functionality, and comfort, delivering users restored mobility and real-life functionality. Kinetic prioritizes innovation and collaboration. They work closely with prosthetists and users to develop executions that meet the unique needs and preferences of each client.
4. Exoskeleton
Exoskeleton 3D printed prosthetics are generally a wearable aid type enhancement to assist with muscle weakness. A variety of companies/research groups such as 3XO, ExoArm and ThirdThumb are leading the development and manufacturing of exoskeletal prosthetic devices. They focus on function, using additive manufacturing technology for client personalization and fast turnaround. These products enhance mobility/strength and improve the quality of life for individuals with limb differences and limb/muscle weakness. Exoskeleton prosthetics teams variously create custom-fit orthotics that are lightweight, durable, and closely tailored to the user's particular needs and anatomy.
Their innovative approaches to design and manufacture incorporate moderate use of advanced materials and smart application of biomechanical principles to deliver effective support and patient-appreciated functionality.
5. Open Bionics Hero Arm
Open Bionics is a particularly famous company, known widely for its innovative Hero Arm, a 3D-printed prosthetic limb that empowers individuals with upper-limb differences. Users commonly report diminished phantom pains and a close neural/emotional interaction with the prosthetic. The Hero Arm stands out for its lightness, design customization, and intuitive control system. This equips users to perform intricate movements with ease.
Open Bionics self-reports a commitment to accessibility, offering affordable prosthetic solutions without compromising quality or functionality. Their Hero Arm aims to be not only functional but also attractive to wear, featuring customizable decorative covers and designs that can reflect the user's personality, much as tattoos might.
6. Low-Cost
Low-cost 3D printed prosthetics are a widespread trend in localized development and manufacture of full prosthetics and components, aiming to improve affordability for developing world amputees. They range from the simplest ‘wooden leg’ devices, through to well-engineered but assertively low-cost hand-built and 3D-printed prosthetics and joints.
7. Cyborg Beast
The Cyborg Beast is a well-reported and widely known product experiment originating with Jorge Zuniga’s research group at Creighton University. They specialized in the development and distribution of the Cyborg Beast 3D-printed prosthetic hand, as a completed product or as a kit set. Derived from open-source designs, the product is notable for its affordability, simplicity, and appreciated functionality. They have carved a place in a complex market by using 3D printing to create lightweight, durable prosthetic hands that are tailored to the needs of users with upper limb differences.
The Cyborg Beast prosthetic offers a moderately customizable design, enabling users to adjust the fit and functionality to suit their physiology, empowering individuals with limb differences to reclaim their independence and enhance their quality of life.
8. Make3D
Make3D is a prominent company specializing in the creation of 3D-printed prosthetic feet. They are appreciated for providing accessible and customizable prosthetics to individuals with limb differences. Make3D utilizes additive manufacturing (and standard parts) to produce prosthetic devices that are highly functional and also affordable, while still managing to be aesthetically satisfying.
Their prosthetics are tailored to the unique needs and physiology of clients, ensuring a comfortable fit and optimized function.
9. UNYQ
UNYQ is an unusual company in that they specialize in customizable covers for prosthetic limbs, rather than whole devices. Their attractive designs combine 3D printing technology with personalized aesthetics to deliver stylish and functional covers. UNYQ offers a range of enhancement options for other suppliers' products, offering elegant and appealing off-the-shelf designs and personalized imaging. UNYQ covers are lightweight, durable, and easy to attach to prosthetics, merging fashion with function.
10. Unlimbited Arm
The Unlimbited Arm is a leading-edge company focused on providing affordable and accessible 3D-printed prosthetic limbs. They offer customizable prosthetic arms that deliver high functionality and user comfort combined with great affordability. The Unlimbited Arm uses 3D printing to create lightweight and durable products tailored to the needs of users with upper limb differences. With a focus on simplicity and ease of use, their products are designed to enhance the mobility and independence of users.
11. Knick Finger
The Knick Finger is an unusual team built around Nick Brookins that it specializes in the production of 3D-printed prosthetic fingers. Their innovative designs target great functionality, user comfort, and good aesthetics. They provide individuals with finger amputations a customizable and affordable solution.
The Knick Finger employs additive manufacturing to create lightweight, durable, and lifelike prosthetic fingers that neatly integrate with the user's hand. With precision and customization, their prosthetic fingers are designed to be adjusted to the specific size and injury level of the user, matching the undamaged nearby digits. Users regain dexterity and confidence in their daily lives.
12. UpYa
UpYa 3D printed prosthetic feet from ExoNeo, another leading company in the development of the sector, is dedicated to providing better-functioning foot prosthetics for those with lower limb loss/difference. They specialize in custom-fit foot prosthetics using additive manufacturing. UpYa's prosthetics are renowned for their high quality, durability, and comfort, allowing users to regain mobility and independence/confidence.
With a commitment to accessibility and affordability, UpYa prosthetics are offered at competitive prices without apparent compromise in performance, comfort, or functionality.
How Much Do 3D-Printed Prosthetics Cost Compared to Traditional Ones?
The price points of 3D-printed prosthetics vary significantly, depending on: materials, complexity, customization, and manufacturing methods. Generally, 3D-printed prosthetics tend to be lower cost than traditionally built devices. This is due to reduced manufacturing lead times, dramatically reduced labor costs, and the ability to customize designs to the user without altering the production processes and costs.
While traditional prosthetics can cost thousands to tens of thousands of dollars, 3D-printed prosthetics may range from hundreds to a few thousand dollars. However, costs range widely based on individual needs and requirements.
Are Traditional Prosthetics More Affordable Than 3D Printed Prosthetics?
Yes. Although the skilled handcrafting required for traditional prosthetics manufacture is generally considerably more costly than the equivalent 3D-printed elements or products, it is worth noting that the more-traditional products win on cost in certain regards. The custom 3D printing of load-bearing joint parts such as knee and ankle joints can be high cost compared with the essentially mass production of these near-standard elements by more traditional means.
Equally, the increasing functionality of certain prosthetics, particularly those for hands/fingers under arm-muscle-sensor control significantly increases the overall cost of these high-functioning prosthetics. This renders the cost differentials between 3D printing and traditional mass production methods less significant. 3D printing offers the greatest cost-effectiveness due to patient-unique and customized parts. However, this means these parts cannot be mass-produced because of the wearer's particular physiology or requirements.
Summary
This article presented the top 3D printed prosthetics, explained each of them, and discussed various companies that manufacture them. To learn more about 3D printed prosthetics, contact a Xometry representative.
Xometry provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities, including 3D printing and other value-added services for all of your prototyping and production needs. Visit our website to learn more or to request a free, no-obligation quote.
Copyright and Trademark Notices
- FDM® is a registered trademark of Stratasys Inc.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.




